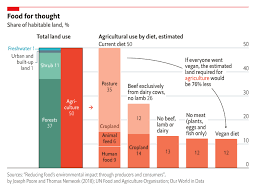
A balanced vegan diet has many benefits. The food list also includes whole grains, legumes, fortified foods, and many other nutritious options. You can also get protein from legumes, as well as iron and choline through nuts. Whole grains are also good sources for fiber. A balanced vegan diet will also be low in fat and cholesterol.
Whole grains are a staple food group
Whole grains are an important part of a vegan diet. They are an excellent source of fiber and nutrients. Whole grains make a great base for baking or salads.
Legumes are high on protein
Legumes provide a great source protein and are a great replacement for red beef. They are high-fiber and low in saturated oil. Peas are rich in protein and fiber. This helps to reduce the risk of developing heart disease.

Fortified foods are rich in iron
Fortified foods can provide iron. Not all fortified foods can be considered equal. There are two types of iron: heme iron, which is found only in animal products, and nonheme iron, which is found in plant foods. Heme iron is less easily absorbed. When you eat a vegan diet, you need to be aware of how much iron your body is absorbing.
Choline can also be found in nuts
Choline can be found in many plant-based foods including nuts. This mineral can also be found in legumes, grains, and legumes. In fact, the National Institutes of Health describes some of these foods as "rich sources" of choline. In fact, some vegetables and beans contain more choline than fish, meat, or dairy products. But, it's important to keep in mind that dairy products contain high amounts of saturated fat which increases your risk of developing Alzheimer's and heart disease.
Zinc is lacking in vegan diets
According to some studies, vegans might need more zinc to keep their bodies healthy. Vegans often don't get enough zinc. There are many ways you can meet your daily requirements for zinc. One of these ways is to eat more fruits and vegetables. You can also consider adding a vegan zinc supplement.
Iron deficiency can impair baby's brain
Iron plays a critical role during brain development in the fetus. Iron is crucial for the hippocampus, which is the time when the brain is still in development. Iron deficiencies in infanthood can affect different areas of the brain depending on the severity and timing. Iron is required by the brain for growth and development. It is vital that expectant mothers provide adequate iron to their baby.
Zinc deficiencies can lead to reduced red blood cell production
Zinc deficiency is most common in infants and older people. Mothers who are pregnant or breastfeeding require more zinc than usual. Zinc, which aids in the growth of the baby, is an essential nutrient for pregnant women. Hypogonadism is a condition where there is a lack of testosterone and impotence. There are approximately 1.1 billion people worldwide who are zinc deficient.
FAQ
How to measure bodyfat?
A Body Fat Analyzer is the best way to measure body weight. These devices are used for measuring the percentage of body fat in people who want to lose weight.
Is being cold bad for your immune system?
According to some, there are two kinds: people who love winter and people who hate it. You may wonder why you feel so miserable in the cold, no matter how much you love or hate winter.
The answer lies in the fact that our bodies are designed to function best during warm weather. Our bodies were designed to thrive in hot weather because this is where the majority of our food sources are.
We live in a very different environment than our ancestors. We spend a lot more time indoors, and are more likely to be exposed to extreme temperatures like heat and cold.
Our bodies aren’t accustomed to extreme temperatures anymore. It means that when we do go outdoors, our bodies feel tired, sluggish even sick.
There are ways to combat these effects though. Staying hydrated is one way to combat this. If you drink plenty of water, you'll help keep your body properly hydrated and flush toxins from your system.
It is important to eat healthy foods. The best way to maintain your body's optimal temperature is by eating nutritious food. This is especially true for those who spend extended periods of time indoors.
Consider taking a few moments each morning to meditate. Meditation can relax your mind and body which can make it easier to deal stress and illness.
How can I get enough vitamins
The majority of your daily nutritional needs can be met solely through diet. Supplements can be beneficial if you are missing a specific vitamin. A multivitamin supplement can provide all the vitamins you require. You can also buy individual vitamins at your local pharmacy.
Talk to your doctor about the best foods for vitamins if you're concerned about not getting enough nutrients. The best sources of vitamins K, E, and C are found in dark green leafy veggies such as spinach and broccoli, kale.
If you are not sure how much vitamin you should be consuming, ask your doctor. Based on your medical history, and current health status, your doctor will recommend the right dosage.
What is the problem of BMI?
BMI stands For Body Mass Index. It is a measurement of body mass based on height and/or weight. BMI is calculated using the following formula:
The weight of a kilogram divided by its squared height in meters.
The result can be expressed as a number, ranging from 0 through 25. A score of 18.5 indicates that you are overweight and a score of 23 indicates that you are obese.
A person of 100kg with a height of 1.75m will have 22 BMI.
Take herbs and other supplements to improve your immunity
To boost immunity function, herbs and natural remedies are available. There are many natural remedies that can boost immunity, including echinacea (oregano), ginger, ginkgo biloba and vitamin C.
These herbs should not be considered as a substitute for conventional medical treatment. These herbal remedies can cause nausea, diarrhea and stomach cramps. They can also cause dizziness, headaches, dizziness, allergic reactions, and stomach pains.
Statistics
- WHO recommends reducing saturated fats to less than 10% of total energy intake; reducing trans-fats to less than 1% of total energy intake; and replacing both saturated fats and trans-fats to unsaturated fats. (who.int)
- WHO recommends consuming less than 5% of total energy intake for additional health benefits. (who.int)
- This article received 11 testimonials and 86% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. (wikihow.com)
- According to the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, a balanced diet high in fruits and vegetables, lean protein, low-fat dairy and whole grains is needed for optimal energy. (mayoclinichealthsystem.org)
External Links
How To
What does "vitamin" actually mean?
Vitamins are organic compounds that can be found in foods. Vitamins allow us to absorb nutrients from food. The body cannot make vitamins; therefore, they must be obtained from food.
There are two types: water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve quickly in water. Some examples include vitamin C,B1 and B2 vitamins (thiamine), B2 and riboflavin, B3 and niacin, B6 vitamins (pyridoxine), B6 vitamins (niacin), folic acids, biotin, pantothenic acids, and Choline. The liver and fatty tissues are home to fat-soluble vitamins. You can find vitamin D, E K, A and beta carotene as examples.
Vitamins can be classified according to biological activity. There are eight major types of vitamins.
-
A - Vital for healthy growth.
-
C - important for proper nerve function and energy production.
-
D - Essential for healthy teeth and bones.
-
E - needed for good vision and reproduction.
-
K - essential for healthy nerves, muscles, and joints.
-
P – Vital for building strong bones.
-
Q – aids digestion and absorption.
-
R – Required for making red blood vessels.
The recommended daily intake (RDA), of vitamins varies with age, gender and physical conditions. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration sets RDA values.
For example, the RDA for vitamin A is 400 micrograms per dayfor adults 19 years or older. Pregnant women require 600 micrograms daily to support fetal development. Children ages 1-8 require 900 micrograms per day. For infants younger than one year, 700 micrograms are required daily. However, this number drops to 500 micrograms each day for children aged 9-12 months.
Children between the ages of 1-18 need 800 micrograms per daily for obesity, while those overweight require 1000 micrograms. To meet their nutritional needs, children underweight and obese need 1200micrograms.
Children ages 4-8 years who have been diagnosed with anemia need 2200 micrograms per day of vitamin C.
2000 micrograms daily is required for adults over 50 to maintain their general health. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding need 3000 micrograms per day due to increased nutrient requirements.
Adults over 70 require 1500 micrograms each day, since they lose approximately 10% of muscle mass each decade.
Women who are pregnant or lactating need more than the RDA. Pregnant women require 4000 micrograms daily during pregnancy, and 2500 micrograms every day after birth. Breastfeeding moms need 5000 micrograms per daily when breastmilk production occurs.